In icd-10-pcs percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of the left vocal cord is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat various conditions affecting the vocal cord. This technique utilizes radiofrequency energy to precisely target and ablate the affected tissue, offering a safe and effective treatment option.
This comprehensive guide delves into the indications, contraindications, preoperative considerations, surgical technique, postoperative care, potential complications, outcomes, and alternative treatments associated with this procedure, providing healthcare professionals with a thorough understanding of its applications and implications.
Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation of the Left Vocal Cord: In Icd-10-pcs Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation Of The Left Vocal Cord

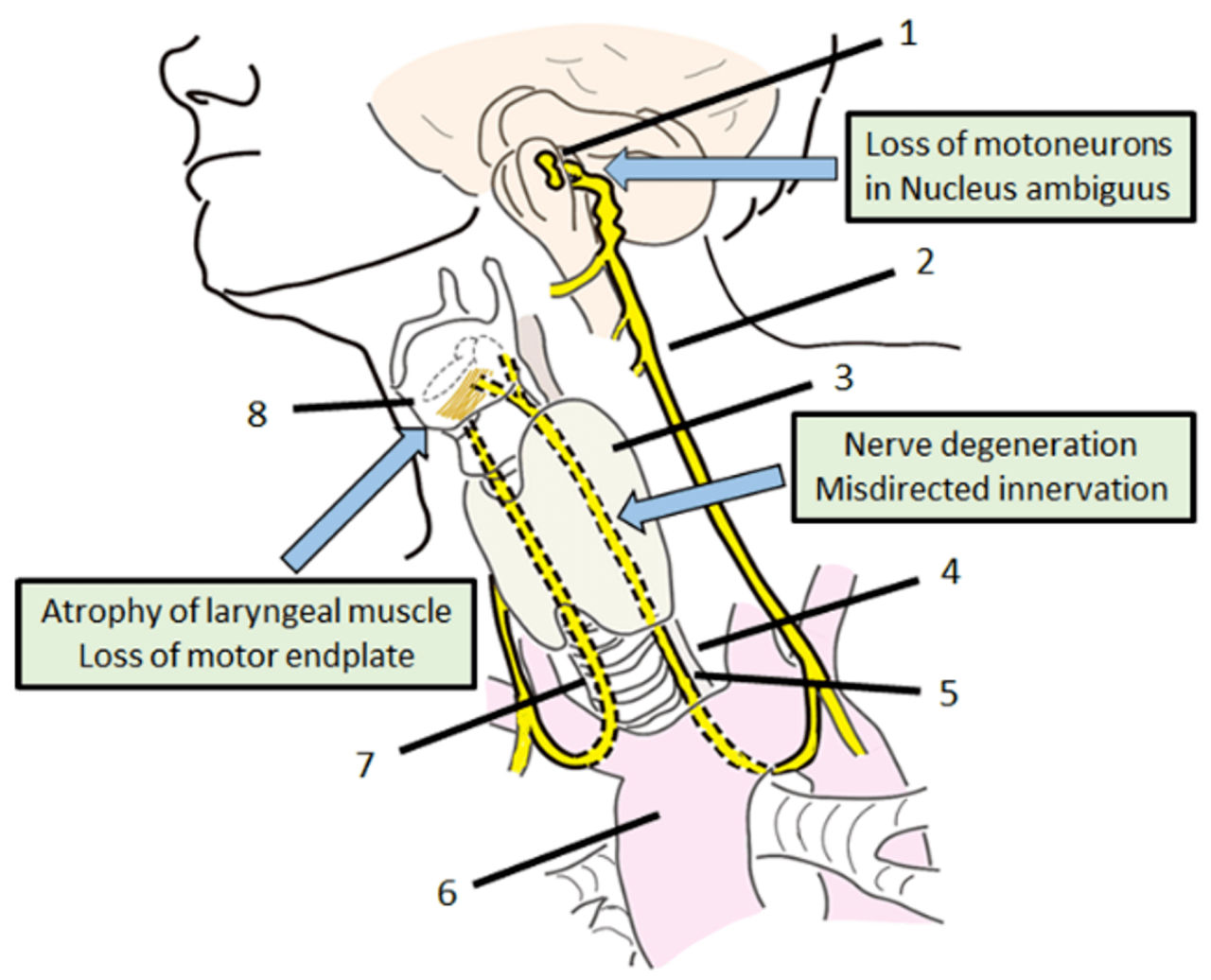
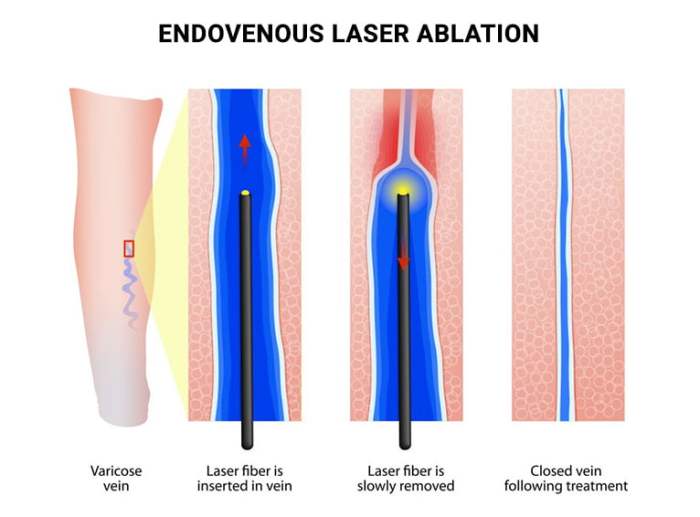
Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation (RFA) of the left vocal cord is a minimally invasive procedure that uses radiofrequency energy to ablate (destroy) the vocal cord. It is performed under local anesthesia and typically takes about 30 minutes to complete.
Indications
Percutaneous RFA of the left vocal cord is indicated for the treatment of the following conditions:
- Left vocal cord paralysis
- Left vocal cord paresis
- Left vocal cord granuloma
- Left vocal cord cyst
Contraindications
Percutaneous RFA of the left vocal cord is contraindicated in the following cases:
- Active vocal cord infection
- Severe vocal cord scarring
- History of vocal cord surgery
- Coagulopathy
Preoperative Considerations
Before undergoing percutaneous RFA of the left vocal cord, the patient will be assessed by a otolaryngologist (ear, nose, and throat doctor). The assessment will include a physical examination of the vocal cords, a laryngoscopy, and a voice evaluation. The patient may also be asked to undergo imaging studies, such as a computed tomography (CT) scan or a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan, to evaluate the vocal cords and surrounding structures.
Surgical Technique
Percutaneous RFA of the left vocal cord is performed under local anesthesia. The patient is positioned supine (lying on their back) with their head extended. A laryngoscope is inserted into the patient’s mouth to visualize the vocal cords. A needle electrode is then inserted through the skin of the neck and into the left vocal cord.
Radiofrequency energy is then delivered through the needle electrode to ablate the vocal cord.
Postoperative Care, In icd-10-pcs percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of the left vocal cord
After percutaneous RFA of the left vocal cord, the patient will be observed in the recovery room for a few hours. The patient will be given pain medication and voice rest instructions. The patient will be discharged home the same day as the procedure.
Complications
The most common complications of percutaneous RFA of the left vocal cord are:
- Hoarseness
- Sore throat
- Bleeding
- Infection
Outcomes
The success rate of percutaneous RFA of the left vocal cord is high. In most cases, the procedure results in a significant improvement in voice quality.
Alternative Treatments
Alternative treatments for the conditions that percutaneous RFA of the left vocal cord is indicated for include:
- Vocal cord injection
- Vocal cord surgery
- Speech therapy
Quick FAQs
What are the common indications for percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of the left vocal cord?
Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of the left vocal cord is commonly indicated for conditions such as vocal cord nodules, polyps, Reinke’s edema, and certain types of laryngeal papillomatosis.
What are the potential complications associated with this procedure?
Potential complications include vocal cord scarring, edema, dysphonia, and aspiration. However, these complications are rare and generally manageable.