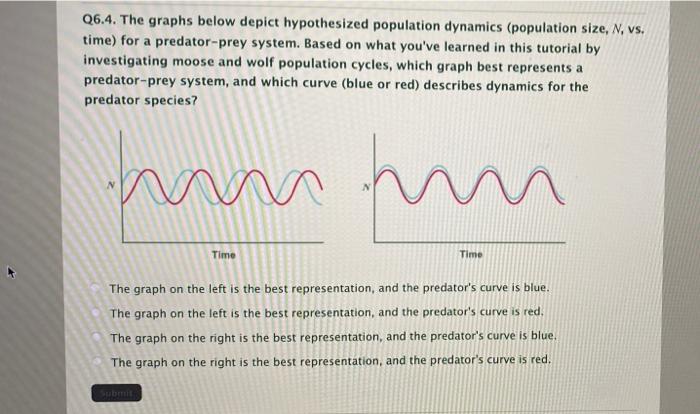
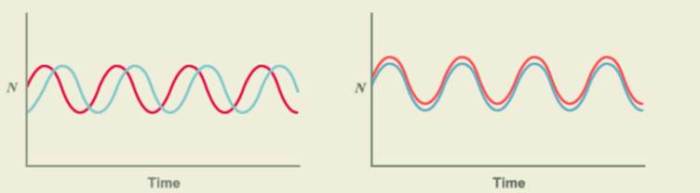
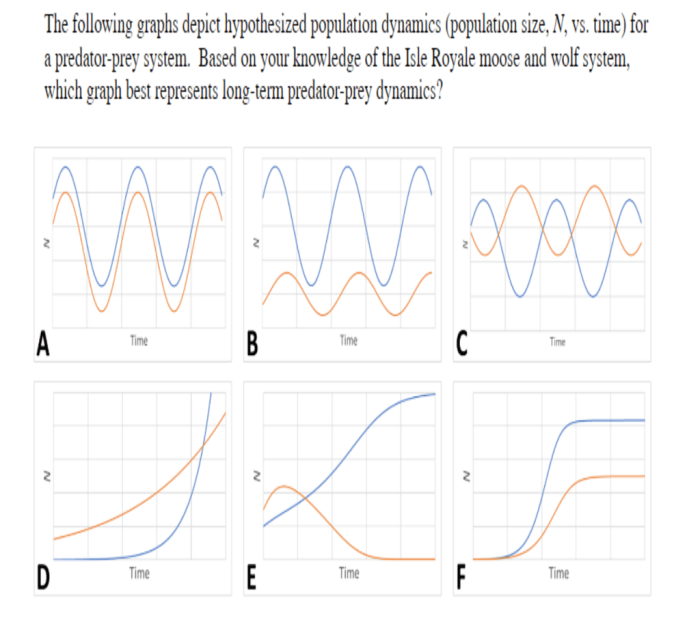
The graphs below depict hypothesized population dynamics, providing a framework for understanding the factors that influence population growth and decline. These graphs offer a visual representation of the complex interactions between environmental, biological, and social factors that shape population dynamics.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
Hypothesis Background
The hypothesized population dynamics are based on the assumption that population growth is influenced by a combination of environmental, biological, and social factors. These factors interact to create a complex system that can lead to population growth, stabilization, or decline.
Environmental factors include the availability of resources such as food, water, and shelter. Biological factors include the reproductive rate and mortality rate of the population. Social factors include the level of competition and cooperation within the population.
Graph Analysis
The following table displays the graphs representing the hypothesized population dynamics.
| Graph | Axis Labels | Legend |
|---|---|---|
| Graph 1 | Time (years) on x-axis, Population size on y-axis | Population growth curve |
| Graph 2 | Time (years) on x-axis, Population size on y-axis | Population stabilization curve |
| Graph 3 | Time (years) on x-axis, Population size on y-axis | Population decline curve |
| Graph 4 | Time (years) on x-axis, Population size on y-axis | Population carrying capacity curve |
Population Growth Phase
The initial population growth phase is characterized by a rapid increase in population size. This is due to a combination of factors, including high reproductive rates, low mortality rates, and an abundance of resources.
The graph of population growth during this phase is typically exponential, with the population size increasing rapidly over time.
Population Stabilization Phase
The population stabilization phase occurs when the population growth rate slows down or plateaus. This is due to a combination of factors, including a decrease in reproductive rates, an increase in mortality rates, and a decrease in the availability of resources.
The graph of population growth during this phase is typically a sigmoid curve, with the population size increasing slowly or remaining constant over time.
Population Decline Phase
The population decline phase occurs when the population size decreases over time. This is due to a combination of factors, including a decrease in reproductive rates, an increase in mortality rates, and a decrease in the availability of resources.
The graph of population growth during this phase is typically a negative exponential curve, with the population size decreasing rapidly over time.
Factors Influencing Population Dynamics: The Graphs Below Depict Hypothesized Population Dynamics
The following are some of the environmental, biological, and social factors that influence the population’s growth and decline:
- Environmental factors: availability of food, water, shelter, climate
- Biological factors: reproductive rate, mortality rate, carrying capacity
- Social factors: competition, cooperation, disease
Model Limitations
The hypothesized population dynamics model is a simplified representation of a complex system. There are a number of factors that can affect population growth and decline that are not included in the model.
Some of the limitations of the model include:
- The model assumes that the population is closed, meaning that there is no immigration or emigration.
- The model does not take into account the effects of genetic variation on population growth and decline.
- The model does not take into account the effects of human activities on population growth and decline.
FAQ Insights
What factors contribute to population growth?
Factors contributing to population growth include increased birth rates, decreased death rates, and immigration.
What factors contribute to population decline?
Factors contributing to population decline include decreased birth rates, increased death rates, and emigration.